Ventral Slot Surgery Dog Complications

Acta Vet. Brno 2008, 77: 269-276
Ventral Slot Surgery Dog Complications Icd 10 Code
Complications Related to Surgical Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Disease in Dogs
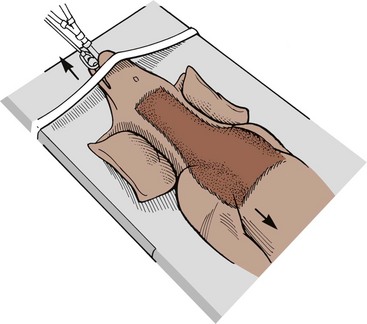
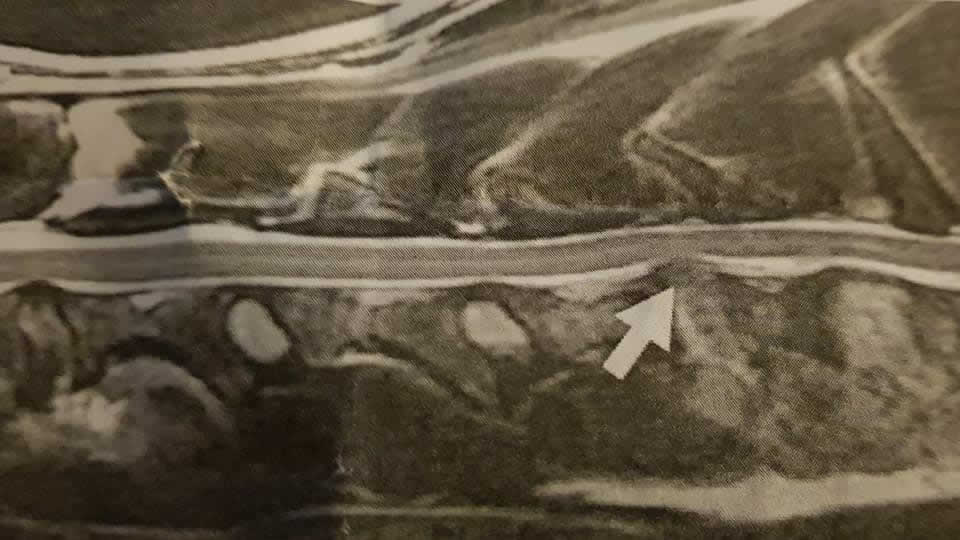
Ventral Slot; Fenestration; The most common surgery for a herniated thoracolumbar disc is the hemilaminectomy. In this procedure, the articular facets (the joint surfaces between vertebrae) are removed and bulging disc material is cleared away from the spinal cord. If a disc in the neck has slipped, then the ventral slot procedure may be performed. The ventral slot uses a throat side approach. This is a preventive procedure often performed on the disk spaces near the herniated space. It involves making a slit over the annulus fibrosus and removal of any mineralized nucleus pulposus. For some patients, this is the only surgery needed but it is not truly a decompressive surgery. On 1/26/2014 my dog had a cervical ventral slot performed at C5-C6 A large amount of fibrous disc material was removed. The C4-C5 and C6-C7 disc spaces were then fenestrated. Following decompression.
After intervertebral disk surgery we often have to deal with various complications (seizures, gastrointestinal tract (GIT) ulcerations, cystitis, and surgical wound healing problems). These complications may lead to the death of the patient. We performed clinical and laboratory investigations in 161 dogs with an intervertebral disc disease. After that, we performed a cranial (n = 31), caudal (n = 125) or both (n = 5) types of myelography at the same time, and surgery - ventral slot decompression (SLOT) (n = 18) or hemilaminectomy (n = 143). During the postsurgical period we observed seizures, GIT complications, cystitis, and surgical wound healing problems or even death of the patients. These complications appeared to be related to the lesion site, the degree of clinical signs and the type of surgical procedure. In our study we found a higher incidence of seizures after cranial myelography, higher incidence of gastrointestinal (GI) complications particularly in paraplegic dogs, and a higher risk of death in patients after the SLOT surgery. The occurrence of cystitis was not significant (p = 0.5524, p = 0.1655, respectively). We consider seizures, GI ulcerations, and death the most frequent complications after intervertebral disc surgery. Their incidence depends on the lesion site and the degree of neurologic symptoms.
Keywords
Ventral Slot Surgery Dog Complications Recovery
Hemilaminectomy, seizures, gastrointestinal ulceration.